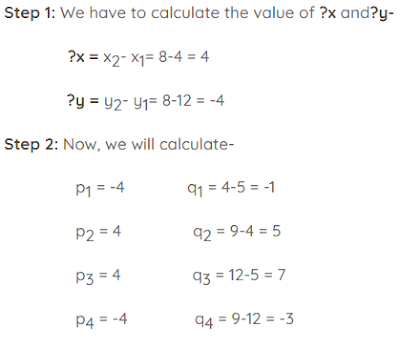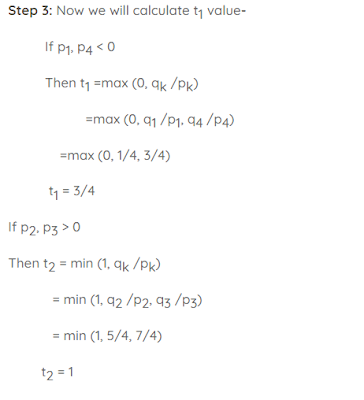Liang Barsky is a line clipping algorithm that is described the window clipping position to clip a line using some parametric inequalities equation. This algorithm is named after You-Dong Liang and Brian A. Barsky. The efficiency of this algorithm is accurate and more than the Cohen Sutherland line clipping algorithm.
Read: Cohen Sutherland line clipping algorithm in Python
Python code for Liang Barsky line clipping algorithm
import PIL.ImageDraw as ID, PIL.Image as Image
# Requirement
# pip install pillow
# im will show the overlapped between lines
# im1 will show the clipped line
im = Image.new("RGB", (640, 480))
im1 = Image.new("RGB", (640, 480))
draw = ID.Draw(im)
draw2 = ID.Draw(im1)
# polygon(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4)
draw.polygon((200, 200, 400, 200, 400, 300, 200, 300), outline=255)
draw2.polygon((200, 200, 400, 200, 400, 300, 200, 300), outline=255)
# define the windows frame
winMinX = 200
winMaxX = 400
winMinY = 200
winMaxY = 300
# Time interval
# Traveling time between initial and finish position
# Initial position
t1 = [0.0]
# Finish position
t2 = [1.0]
# Handling the float numbers
def ROUND(a):
return int(a + 0.5)
def clipTest(p, q, t1, t2):
retVal = 1
# 4. calculate the value of pk and qk
if p < 0.0:
r = float(q) / float(p)
if r > t2[0]:
retVal = 0
elif r > t1[0]:
t1[0] = r
elif p > 0.0:
r = float(q) / float(p)
if r < t1[0]:
retVal = 0
elif r < t2[0]:
t2[0] = r
elif q < 0.0:
retVal = 0
return retVal
def LiangBarskyAlgo(x1, y1, x2, y2):
# 3. calculate the values of t1 and t2
t1 = [0.0]
t2 = [1.0]
dx = x2 - x1
# 2. Calculate the value of p1, p2,p3, p4 and q1, q2, q3,q4.
if clipTest(-dx, x1 - winMinX, t1, t2):
if clipTest(dx, winMaxX - x1, t1, t2):
dy = y2 - y1
if clipTest(-dy, y1 - winMinY, t1, t2):
if clipTest(dy, winMaxY - y1, t1, t2):
if t2[0] < 1.0:
x2 = x1 + t2[0] * dx
y2 = y1 + t2[0] * dy
if t1[0] > 0.0:
x1 = x1 + t1[0] * dx
y1 = y1 + t1[0] * dy
draw2.line((ROUND(x1), ROUND(y1), ROUND(x2), ROUND(y2)), fill=(0, 255, 0))
# Begin the clipping process
def clip(x1, y1, x2, y2):
# Draw the intersection line
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y2), fill=(0, 255, 0))
# Perform Liand Barsky Alogorithm to get the clipped line
LiangBarskyAlgo(x1, y1, x2, y2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1. Set the endpoints of the line (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
# two points need to draw a line
# point 1
x1 = int(input("Point1 x1: "))
y1 = int(input("point1 y1: "))
# point 2
x2 = int(input("Point2 x2: "))
y2 = int(input("Point2 y2: "))
# Checking if the line need to be clipped or not?
clip(x1, y1, x2, y2)
# Show the images and save them locally
im.show()
im.save('1. Line with Rectangle overlapped.png')
im1.show()
im1.save('2. Clipped line after algorithm applied.png')
Input
Point1 x1: 123
point1 y1: 123
Point2 x2: 789
Point2 y2: 789
Output
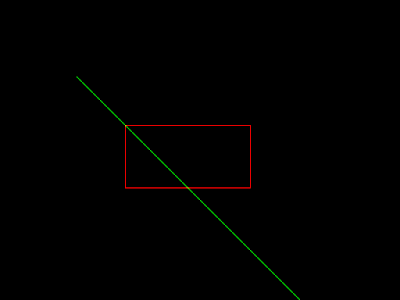
1. Line with Rectangle overlapped.png 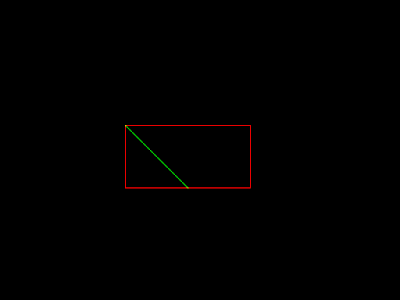
2. Clipped line after algorithm applied.png
Solved examples of Liang Barsky line clipping algorithm
Problem statement:
Solution:
.png)