A system must be able to get data quickly to be useful. For this, the understanding of abstraction level in database management systems (DBMS) must be clear. Three types of abstraction levels exist in DBMS. Designers have used complicated data structures to represent data in databases due to the necessity for efficiency. Because many database-system users aren't good with computer technology, developers utilize various levels of abstraction to disguise the system's complexity from users, making it easier for them to work with it.
Types of Data Abstraction
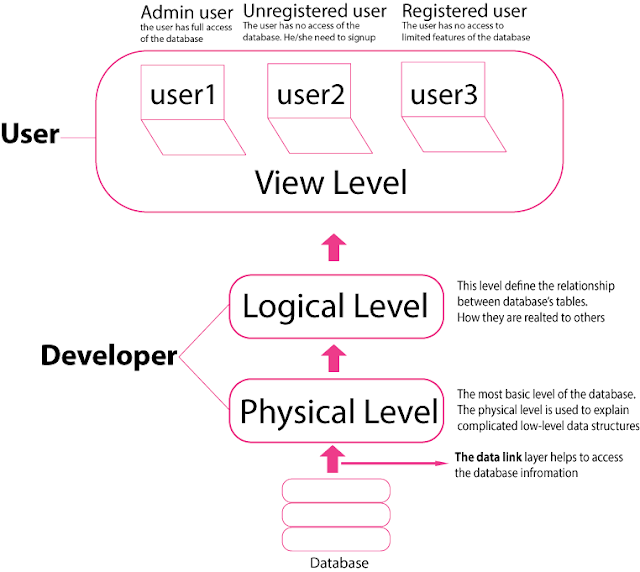
Fig. 01: A full view of the data abstraction level of DBMS with detailed information.
Physical level: The most basic level of abstraction specifies how data is stored. The physical level is used to explain complicated low-level data structures. The data link layer and the network layer of the network section send the data to this view, then the physical level is received the data and is processed for the transmission media. This layer is a little bit responsible for the speed to access the database's information.
Logical level: The next level of abstraction explains what data is kept in the database and how those data are related to one another. As a result, the logical level explains the whole database in terms of a small number of very straightforward structures. Although complicated physical-level structures may be involved in the execution of basic structures at the logical level, the user of the logical level does not need to be aware of this complexity. Physical data independence is the term for this. The logical degree of abstraction is used by database managers when deciding what information to maintain in the database. Database managers carefully design the connections among tables of the database. The security of the database can be defined at this level.
View level: Only a portion of the database is described at the greatest level of abstraction. Even if the logical level employs simpler structures, the diversity of information recorded in a big database adds to the complexity. Many database system customers may not want all of this information; instead, they just require access to a portion of the database. This process is done by the back-end and front-end developers carefully. Most of the security of the database is defined by this by the developers.
The view abstraction level exists to make their interaction with the system easier. For a certain database, the system may give multiple views.
The multiple views of this level are divided into three particular views.
Admin user: The user can access the full database system and handle the unregistered and registered user. What they can see and what they can do with the database's shared limited portion. 100% of the database was modified by this user.
Unregistered user: The user in this level is called a new user and they need to be registered with certain conditions. They have no access to modify any data in the database.
Registered users: They need to share the information to be loyal to the database with certain conditions. The user is able to modify the limited features of the database.
Read Similar Posts