Introduction
 |
| icon is taken from pngpath.com |
Fractional Knapsack is a very famous problem for the greedy algorithm. Suppose a thief breaks into a grocery store. There are many kinds of items, such as wheat, rice, salt, and many more. Now, he can't steal everything. Because the bag has a capacity of only 10 kg. So how can he be profitable if he steals? The solution is very simple. The item that costs the most, he will start taking that thing first. If he sees that the item is over and there is still some space left in the bag, then he will start taking the next expensive item. This way he will continue to carry his work until his bag runs out of capacity. This problem is called Fractional Knapsack.
Example of Fractional Knapsack
Suppose, the grocery store has 5 items (item 1, item 2, item 3, item 4, item 5) and the thief will choose the item according to the Factional knapsack procedure.
Now, the unit price ( price/weight) will be calculated.
We will rearrange the item list according to the unit price ratio of items
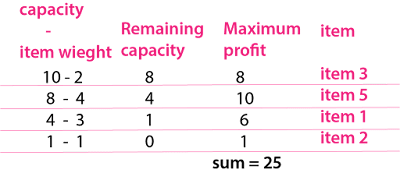
Take the most valued unit price in the bag and decrease the capacity one by one. In the meantime, we will add the item's price in the maximum profit column.
Notebook: As only 1 kg is left in the bag, so we choose item 2 and take 1 kg (price 5/5=1) from this.
The solution to this problem is given below in C++ and Python programming. I hope, this will help you.
Fractional Knapsack in C++
Fractional Knapsack in Python
def fractional_knapsack(weights, prices, capacity):
MP = 0
for wieght_price_pair in sorted(zip(weights, prices), key=lambda x: - x[1] / x[0]):
if not bool(capacity):
break
if wieght_price_pair[0] > capacity:
MP += int(wieght_price_pair[1] / (wieght_price_pair[0] / capacity))
capacity = 0
elif wieght_price_pair[0] <= capacity:
MP += wieght_price_pair[1]
capacity -= wieght_price_pair[0]
return int(MP)
capacity=int(input("Enter the capacity: "))
weights=list(map(int, input("Enter the weights: ").split()))
prices=list(map(int, input("Enter the prices: ").split()))
MP=fractional_knapsack(weights, prices, capacity)
print("Maximum Profit: ", MP)